Understanding UML at a Glance
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) provides different diagram types to visualize systems from multiple perspectives. While class diagrams focus on a system’s static structure, other diagrams capture behavior, interactions, or workflows. Knowing the distinction helps you choose the right diagram for your design goals.
Class Diagrams: The Structural Blueprint
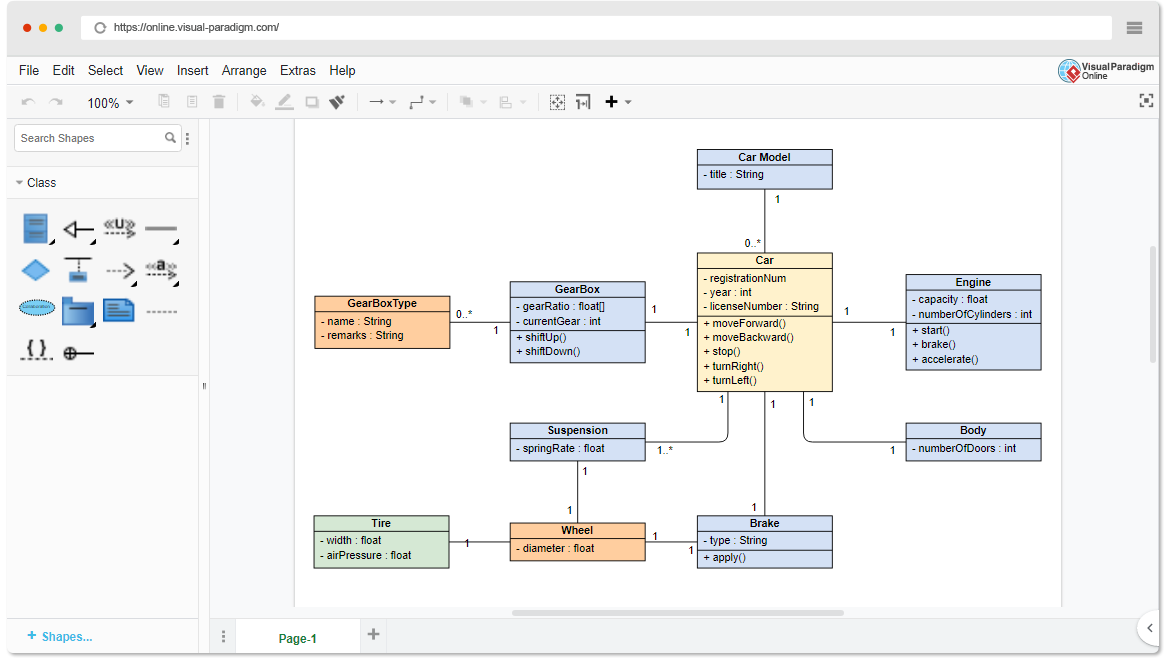
A class diagram represents the building blocks of a system — its classes, their attributes, operations, and the relationships between them. It is most useful for:
- Designing object-oriented systems
- Mapping domain models
- Planning database structures
- Documenting system architecture
Online Class Diagram Maker
Sequence Diagrams: Interactions Over Time
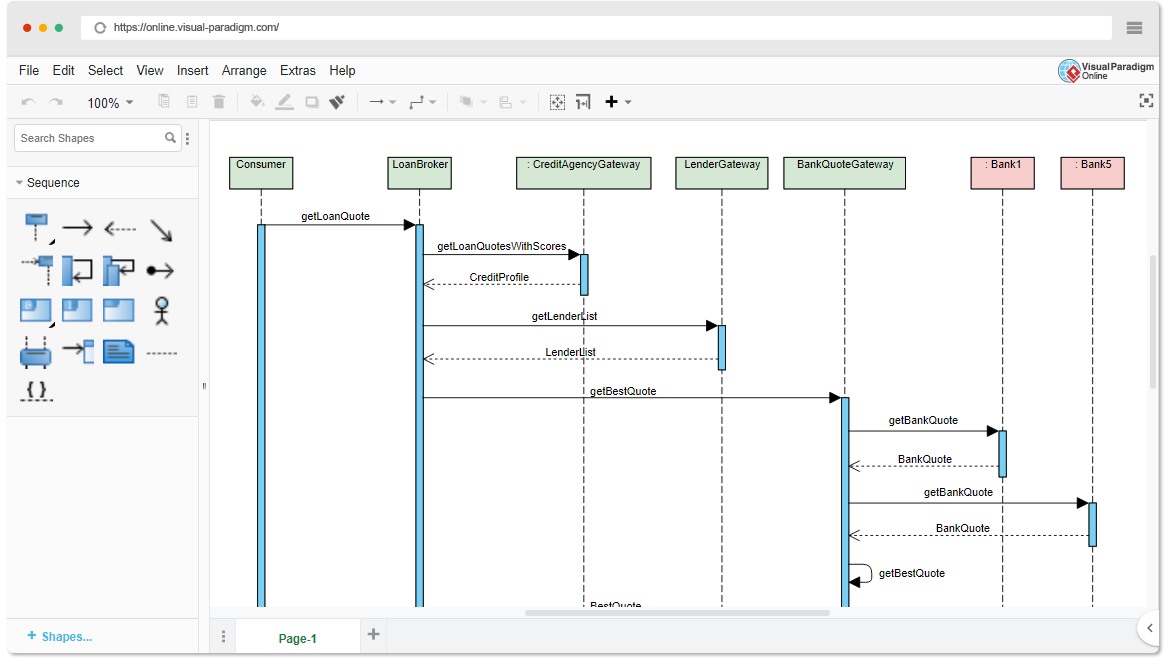
A sequence diagram focuses on the flow of messages between objects in a specific scenario. It is ideal for:
- Understanding how parts of the system communicate
- Capturing step-by-step interactions for a use case
- Identifying dependencies between components
Online Sequence Diagram Maker
Activity Diagrams: Mapping the Workflow
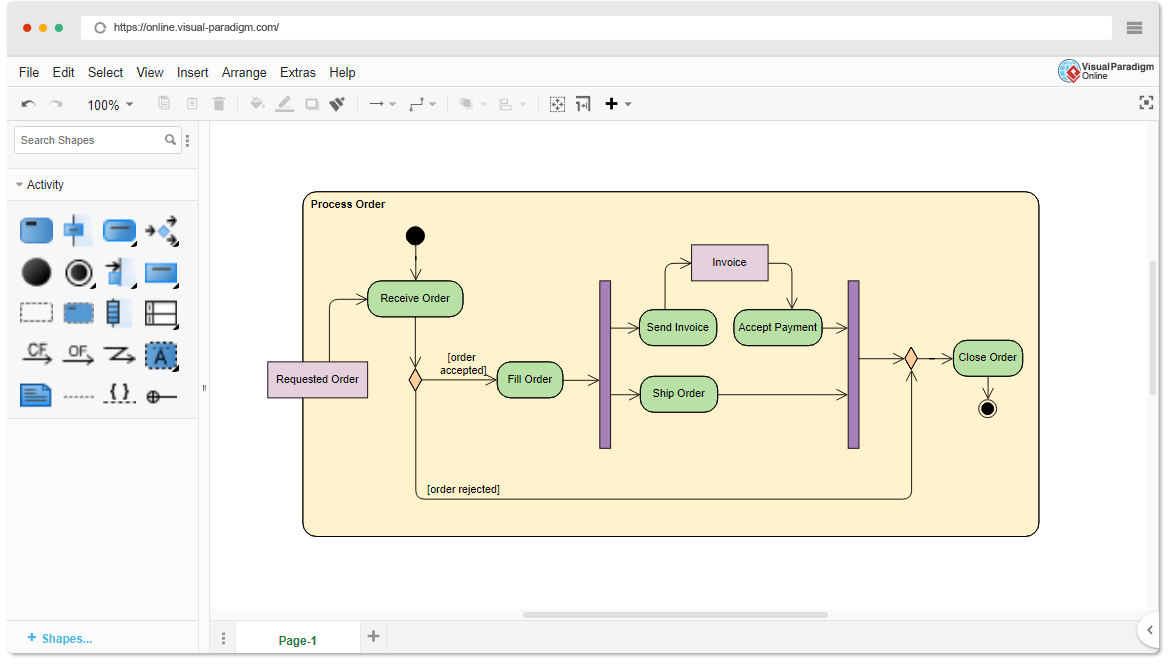
An activity diagram illustrates the flow of control or data in a process. It works well for:
- Modeling business processes
- Visualizing decision points and branching paths
- Analyzing operational workflows before coding
Online Activity Diagram Maker
Use Case Diagrams: High-Level System View
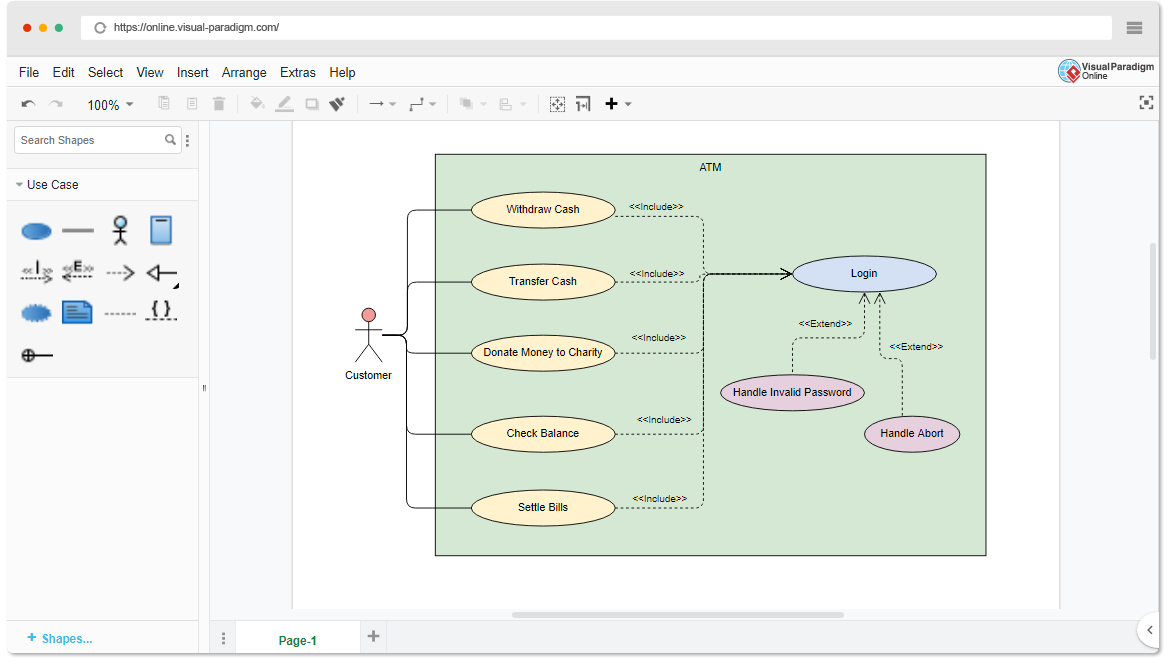
A use case diagram shows the functional requirements of a system from the perspective of end users (actors). It is best suited for:
- Capturing system goals
- Identifying main user interactions
- Starting point for further detailed diagrams
Online Use Case Diagram Maker
Which One Should You Use?
The right diagram depends on where you are in the development lifecycle and the type of details you want to highlight.
- Structure? Use a class diagram.
Ideal for the early design phase when you need to define the system’s building blocks. A class diagram lays out the entities, their properties, and how they connect — serving as the foundation for further modeling and coding.
- Interaction sequence? Use a sequence diagram.
Best for exploring a specific feature or scenario in detail. A sequence diagram shows how objects communicate step-by-step, which is especially helpful for debugging logic or explaining a process to a developer.
- Workflow logic? Use an activity diagram.
Suited for understanding processes from start to finish. Activity diagrams help spot inefficiencies, identify decision points, and ensure all possible paths are accounted for before implementation.
- User perspective? Use a use case diagram.
Great at the very beginning of a project to capture functional requirements. Use case diagrams focus on the goals of the system and how different actors (users or external systems) will interact with it.
In many projects, you will use several UML diagrams together — starting with a class diagram for the system’s structure, then adding others to clarify behavior, workflow, and user interaction.

Speeding Up the Process with AI
No single UML diagram fits every purpose. By combining the right diagram types — starting with a class diagram for structure — you can create a well-rounded, clear representation of your system. AI tools make this process faster, more consistent, and less error-prone.
Instead of creating diagrams manually from scratch, modern tools like Textual Analysis AI Class Diagram Generator can turn a simple problem description into a complete class diagram in minutes. From there, you can connect your design to other UML diagrams for a complete system model.
 Visual Paradigm Desktop |
Visual Paradigm Desktop |  Visual Paradigm Online
Visual Paradigm Online



