Why Compare UML Diagrams?
UML offers multiple diagram types, each highlighting different aspects of a system. While they may overlap, they serve unique purposes. Knowing when to use sequence diagrams versus other UML diagrams helps avoid redundancy, ensures clarity, and improves collaboration.
Sequence Diagrams – The Flow of Interactions
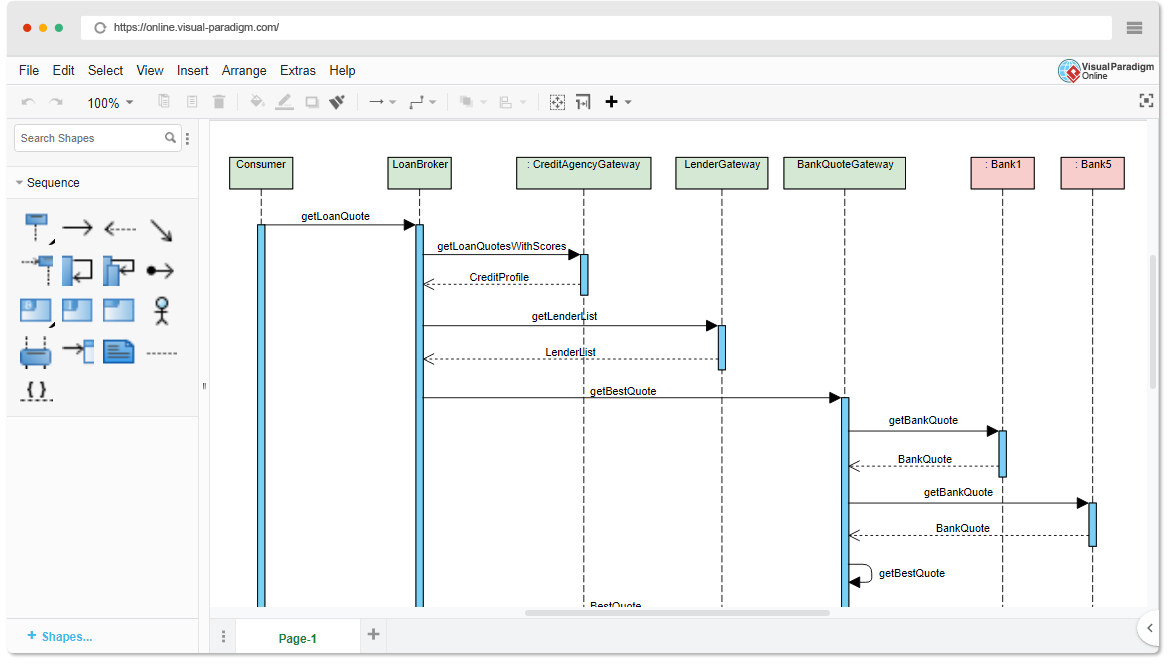
Sequence diagrams focus on time-ordered communication between actors and system components. They are best for:
- Showing how tasks are completed step by step
- Capturing real-time messaging in distributed systems
- Translating use case descriptions into executable flows
They shine when you want to emphasize when and how components exchange messages.
Learn More
Use Case Diagrams – Defining System Scope
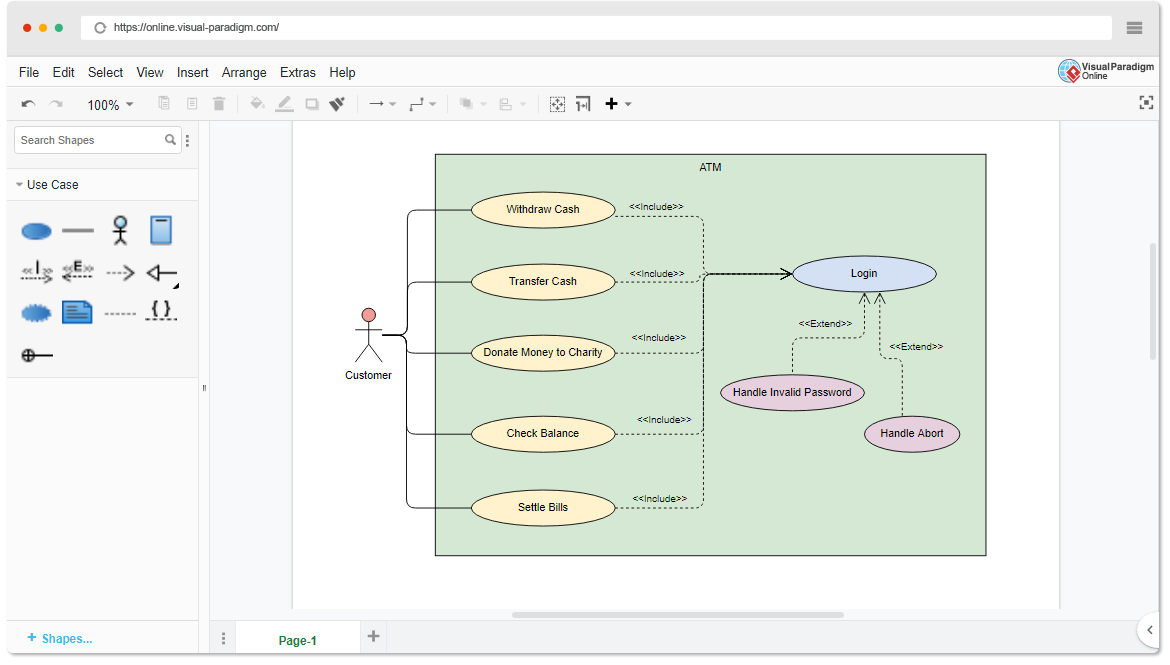
Use case diagrams highlight who interacts with the system and what goals are achieved. They do not explain how processes unfold internally. Ideal for:
- Defining project boundaries
- Aligning stakeholders on system functionality
- Providing input for detailed diagrams such as sequence diagrams
Learn More
Activity Diagrams – Modeling Workflows
Activity diagrams represent control flow and business processes. Unlike sequence diagrams, they do not focus on lifelines or messaging order. Best for:
- Capturing decision points, loops, and concurrent processes
- Explaining business workflows before diving into technical design
- Serving as a bridge between requirements and behavioral models
Learn More
Class Diagrams – Defining Structure
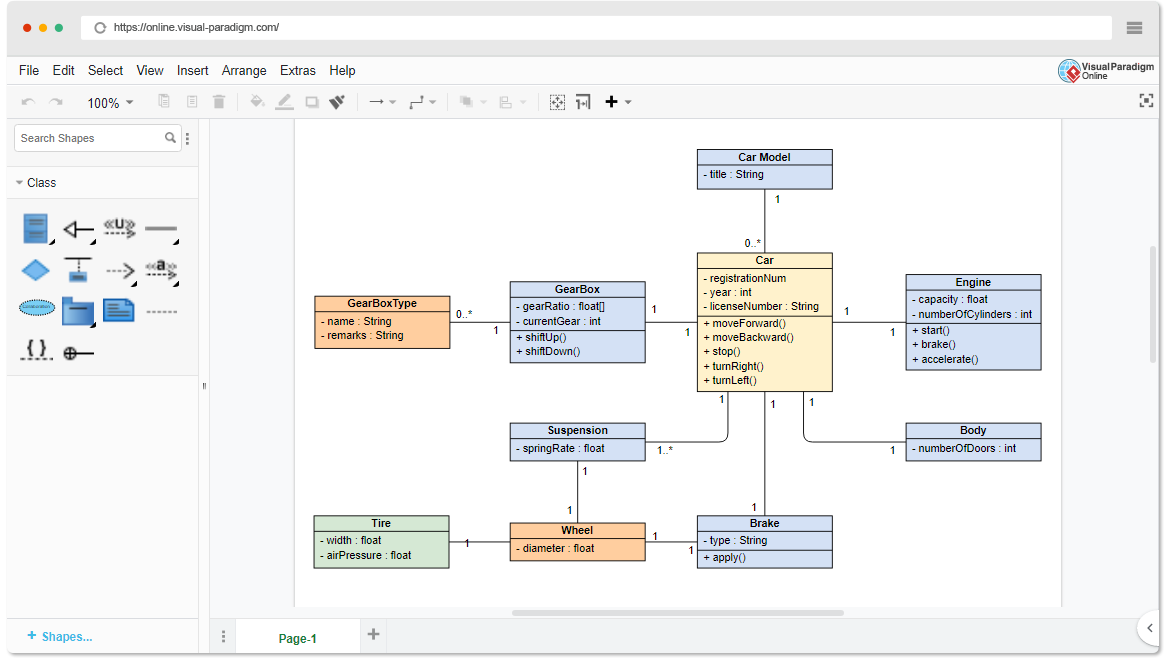
Class diagrams show the static structure of a system, including classes, attributes, methods, and relationships. While sequence diagrams show behavior, class diagrams focus on:
- Data modeling and object relationships
- Identifying entities and their responsibilities
- Forming the foundation for database and code generation
Learn More
Choosing the Right Diagram
- Start with use case diagrams for scope and actors.
- Use activity diagrams for workflows and logic.
- Apply sequence diagrams for time-ordered interactions.
- Build class diagrams for structural detail.
 Visual Paradigm Desktop |
Visual Paradigm Desktop |  Visual Paradigm Online
Visual Paradigm Online


